A Step-by-Step Guide to Infant CPR
A Step-by-Step Guide to Infant CPR

by Greta Kviklyte
Life Saver, AMC
Co-authored by Kim Murray, RN, M.S.
posted on Apr 10, 2024, at 12:26 am
Out-of-hospital cardiac arrests, a vital aspect of emergency medicine with heart resuscitation and oxygen administration involved, affect about 300,000 people in the United States each year; this emphasizes the need to know local emergency numbers and clinical practice guidelines. The survival rate for these patients in emergency medicine (the ones needing resuscitation or suffering from infectious diseases, heart issues, or otitis media) is typically low at approximately 8% in clinical practice.
Patients suffering from in-hospital cardiac arrests, specifically those involving the heart and lungs, form a notable subset of cases encountered in the domains of general and thoracic surgery. These instances are pivotal of emergency medicine, requiring dedicated clinical strategies that integrate context-specific knowledge and experience for effective management.
We offer Online CPR and BLS Certification
According to CPR.Heart.Org, more than 7,000 children, inclusive of infant cases, suffer an out-of-hospital (OOH) cardiac arrest annually, and survival rates average 6.2% for those less than one year old. As with all cardiac arrest cases, immediate intervention, including the steps listed in the lesson available here, is necessary to reduce risk of death, and health professionals, parents, and anyone involved in lives of infants and children need to understand the basics of infant CPR, how to apply two person CPR to small children, and how to improve your training for such circumstances with a few tips.
The Risk of Cardiac Arrest in Infants and Children
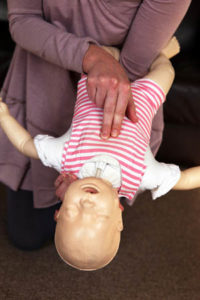
Cardiac arrest often occurs in children, including babies, as a result of pre-existing heart conditions. In most cases, unintentional chokingand suffocation typically precipitate cardiac arrest in infants under age one. Choking is the fourth leading cause of death in children under age five, and toys, household items, cookies, and food present possible choking hazards. Sadly, mortality rates are grim; a baby under the age of one dies every five days due to choking on items like cookies, reports the New York State Department of Health.
What are the Causes of Infant Cardiac or Respiratory Arrest?
The causes of infant cardiac or respiratory arrest mirror those of the H’s and T’s of reversible causes of arrest. These are explained in further detail in this learning module. For reference, these include:
- Hypovolemia: A significant decrease in blood volume leading to inadequate circulation
- Hypoxia: The lack of sufficient oxygen reaching the tissues.
- Hydrogen Ion Buildup or Acidosis is an excess of acid in the body that can disrupt cellular function.
- Hypo/Hyperkalemia: Abnormal levels of potassium in the blood are too low (hypo) or high (hyper)..
- Hypoglycemia: Low blood sugar levels can impair brain function and metabolism.
- Hypothermia: Dangerously low body temperatures that affect the heart’s rhythm and function
- Tension Pneumothorax: Severely collapsed lung causing increased pressure within the chest, affecting the heart, eventually leading to cardiac arrest as well as circulatory collapse..
- Tamponade, Cardiac: Pressure on the heart is caused by fluid accumulation, preventing it from pumping effectively.
- Toxins: Poisonous substances that can lead to cardiac or respiratory failure.
- Thrombosis of Coronary and Pulmonary Vessels: Blood clots formed within arteries depriving organs of oxygenated blood supply
- Unrecognized trauma: Physical injury not immediately evident but may cause cardiac or respiratory distress later on.
These are just a few examples, so don’t get caught up trying to memorize them all. Apply your critical thinking skills and try to figure out why each “cause” could end up being an effect of something else entirely. For example, choking is considered trauma, while electrocution could cause a cardiac tamponade. However, we’ll learn how these present themselves shortly.
Remember… if you can’t find a pulse, you must start compressions immediately! But what if you do find a pulse? Do we stop compressions until they’re gone again? Not at all!
Essential Steps for Performing CPR on Infants and Small Toddlers
The fundamentals of CPR and life-saving measures are similar to those of adults, but due to the smaller stature of children and infants, time is even more vital than ever.
Additionally, an infant is unable to voice his or her pain or complaints, so it is up to the informed responder to act.
If the infant does not respond to stimuli or if the child only appears to be gasping for air begin CPR immediately.
The infant CPR and Basic Life Support (BLS) algorithm can be easily remembered with this acronym:
– S (Screaming) Is the child crying normally?
– A (Alertness) Is the child alert?
– P (Painful Stimuli) Does the child respond to painful stimuli such as a sternal rub?
– M (Moving and Breathing) Is the child moving and breathing spontaneously?
- In these first few steps, we ensure no immediate dangers around us. Choking or trauma are common causes of cardiac or respiratory arrest in infants so always keep it in mind. After this, we need someone to call emergency medical services because every second counts counts.
- You should also try seeing if the baby responds by calling their name loudly, and tapping their feet gently so they know they’re safe. If you notice something wrong when you approach them alone, you should take them with you while seeking help, especially if advanced care needs are urgent unless the head injury is suspected, in which case avoid moving them until EMS arrives.
- When assessing breathing, look for chest movement while listening to breathing sounds and feeling airflow near the mouth area.
- Quickly check their carotid artery located on either side of their neck for a pulse taking no longer than 10 seconds.
- Start doing chest compressions: If there’s no response or breathing, begin pushing down on their chest hard and fast. Do so at a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute, with each compression about two inches deep on infants.
- Open their airway and give rescue breaths: Tilt the head back slightly and lift the chin to open the airway. Give them two rescue breaths for every 30 chest compressions. Or if you’re doing two-person CPR, do it for every 15 compressions instead.
- CPR without full respiration: If the infant has a pulse but weak breathing, give it one breath every three to five seconds until it can breathe normally again.
- Keep track of everything: After doing CPR for five rounds, recheck the child’s pulse. Do chest compressions if they turn bluish due to lack of oxygen./li>
- Using an AED: If you have access to an automated external defibrillator (AED), use pads made specifically for children or use a child-sized pad as long as it fits right. Follow what it tells you carefully and continue with CPR for another two minutes before checking them over again.
- Continue following AED instructions: Keep following whatever the AED tells you, even if the rhythm is shockable or not until real help arrives or they wake up on their own.
Infant CPR Ratio
There are two types of Infant CPR: the “1 Rescuer” and the “2 Rescuers,” one when you’re alone and the other when you have a partner. Both sequences are designed to keep blood circulating throughout the body.
The 1 Rescuer ratio is done to avoid confusion, using a 30 chest compressions to 2 rescue breaths pattern. After pressing down on their chest with a gentle thumb thirty times, breathe into them twice by tilting their head back to open up both nostrils and mouth. Continue this cycle of thirty compressions and two breaths until further help arrives, or they show signs of life.
When working with someone else, it’s important to be as efficient as possible to save time. The 2 Rescuers CPR shifts the compression-to-breath pattern from 30:2 to a more frequent rate of 15:2. This makes sure that one person isn’t hogging all the airtime while another performs compressions.
Compression uses the two-thumb technique to apply more pressure without hurting them. After twenty compressions, one rescuer will give two breaths, then switch off with the other partner, who will proceed with fifteen more.
These methods are meant to be easy enough for anyone to understand but still effective for saving an infant’s life whether you work alone or side by side.
Common Mistakes During Infant CPR
The biggest mistake made when performing infant CPR is failure to initiate chest compressions properly. It is easy to panic, and time lost increases the risk of poor outcomes.
The other mistake involves positioning the infant for chest compressions. There are two acceptable means.
- Place the infant on his back or a firm surface. Using two fingers in the center of the chest and slightly below the nipple line, press down approximately 1.5 inches.
- The two-thumb encircling technique is also acceptable for chest compressions in infants. Position yourself at the infant’s feet. Place your thumbs side by side in the center of the infant’s chest and slightly below the nipple line, explainsNationalCPRAssociation.com. Wrap your fingers around the infant’s chest to support the back. Use the thumbs to administer chest compressions.
For those using the two-thumb encircling technique, only use the force of your thumbs to administer compressions. Squeezing the infant with your fingers will result in insufficient chest recoil and a higher risk of injury.
Another mistake occurs when attempting to determine if a diminished pulse should require the initiation of chest compressions. In children, a pulse of less than 60 beats per minute, which meets the bradycardia criteria, is considered pulseless electrical activity. As a result, begin CPR if the infant has a pulse of less than 60.
For those with limited experience or training in infant CPR, follow the hands-on approach. The rate of compressions is still 100-120 per minute, but you must follow the guidelines for using two fingers or the two-thumb encircling technique to administer compressions.
If you prefer to use a mask, ensure it does not cause any delays in care. Additionally, the mask should not inhibit your ability to obtain a proper seal for administering rescue breaths.
What About Infants That Are Choking
A choking infant carries a few distinctions from performing choking care to toddlers and older children. When the airway is blocked, an infant may gasp or appear motionless. Infants have the highest risk of choking due to their tendency to put small objects in their mouths, which is explainedhere.
When a mild choking incident occurs, and the child can still breathe, it’s important to stay with the infant and try to keep him calm. If the obstruction cannot be cleared quickly or leads to additional breathing problems, make sure to call EMS.
In cases of severe obstruction, characterized by an inability to make noise, failure to breathe, or the appearance of cyanotic symptoms, immediate intervention is critical and follows the outlined steps:
- Holding the infant in your lap, rest the infant’s chest on your forearm, keeping the head lower than the chest. Ensure your hand is placed on the chest and does not cause distress to the infant’s neck.
- Using the heel of the hand, perform five back slaps in a downward, firm motion between the infant’s shoulder blades.
- Move the baby to the other arm, placing the baby on his back. Provide five thrusts to the chest, mirroring chest compressions during CPR. If the infant does not clear the obstruction, use both arms, swap the infant back to the other arm, and put the baby face down again.
- Between cycles, look in the infant’s mouth for any object. Never Perform A Blind Finger Sweep Unless You See An Object That Can Be Removed. Blind sweeps risk pushing the object further down into the throat and worsening the situation.
- The situation becomes more urgent if the baby stops responding and cannot clear the object. Yell for a bystander to contact EMS. Begin infant CPR. After the first cycle of 30 compressions, or 15 compressions if performing 2-person CPR, check the infant’s mouth for an object. If the object can be seen, remove it. Otherwise, continue CPR. Attempt to perform rescue breaths for the duration of the event.
How to be Prepared for Infant CPR Training
No one wants to think about what you’d do if a baby starts choking or goes into cardiac arrest. But it’s good to know what you would do. Statistics tell us that the baby will only choke mildly in most cases. Even still, when you have a mild obstruction, there is a possibility of becoming severely obstructed even within just 30 seconds, and this is now a life-threatening emergency.
To remember the skills taught in an infant CPR and choking course, try these:
- Make sure they use appropriate-sized manikins.
- Observe variances in speed, depth, and standards from adult CPR.
- Think of what babies can choke on (food, toys) and apply while looking for obstructions.
- Use interactive tools (videos, demonstrations) for long-term memory skills.
- Bradycardia with a pulse <60 is PEA in infants-toddlers-children until adolescence.
- Treat for trauma-induced causes as part of the PALS algorithm/infant CPR+BLS process.
- As soon as possible get an AED for any emergency.
- If severe obstruction cases regain consciousness/circulation, they need to see an MD (to rule out aspiration of contents into the lungs).
- Never blind finger sweep on the infant.
Know How to Reduce Infant Mortality With the Right CPR Courses Now
The mortality risk for infants that suffer OOH cardiac arrest is significant. Immediate intervention is crucial for the greatest chance of survival when an infant suffers arrest due to any reversible cause or choking. Babysitters, retail staff, and anyone involved in child care should learn how to perform infant CPR. Understanding its urgency is vital.
Also, remember to enroll in your life-saving skills course, available online at Advanced Medical Certification, and share this article and your thoughts to social media now. Together, we can make a difference and save lives!




 If you’re looking to get started in the healthcare field, obtaining a BLS and CPR certification is a great place to begin. These certifications provide individuals with the most up-to-date medical guidelines and the skills necessary to respond to emergencies and save lives. Unlike more advanced certifications like ACLS, BLS training is accessible to anyone, even those without prior experience in the field. Having a BLS certification can give you a competitive edge and set you apart from other job applicants, even before your nursing career takes off.
If you’re looking to get started in the healthcare field, obtaining a BLS and CPR certification is a great place to begin. These certifications provide individuals with the most up-to-date medical guidelines and the skills necessary to respond to emergencies and save lives. Unlike more advanced certifications like ACLS, BLS training is accessible to anyone, even those without prior experience in the field. Having a BLS certification can give you a competitive edge and set you apart from other job applicants, even before your nursing career takes off. BLS certification may not be a requirement for all entry-level positions in healthcare settings, but CPR training is always a must. For instance, skilled nursing facilities, or “nursing homes,” may employ individuals who are not BLS certified, and various requirements may vary per case, but
BLS certification may not be a requirement for all entry-level positions in healthcare settings, but CPR training is always a must. For instance, skilled nursing facilities, or “nursing homes,” may employ individuals who are not BLS certified, and various requirements may vary per case, but 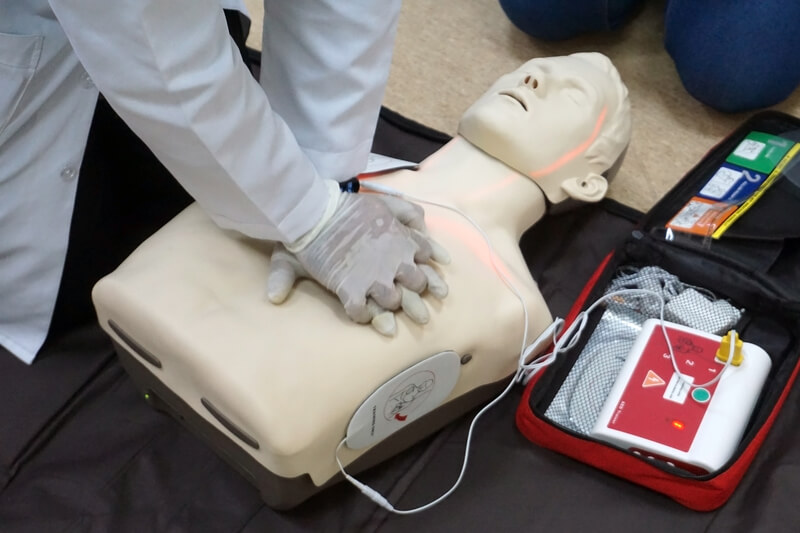 Our online basic life support training includes a free textbook that is accessible online. Learn everything there is to know about up-to-date BLS for individuals in all scenarios. Train and prepare using
Our online basic life support training includes a free textbook that is accessible online. Learn everything there is to know about up-to-date BLS for individuals in all scenarios. Train and prepare using  Take a look at the
Take a look at the 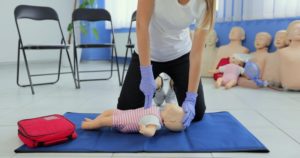 Pediatric Advanced Life Support is a series of skills and techniques necessary for saving the lives of infants and children. If you are ever in a situation where a small child is choking or struggling to breathe or may be unconscious, PALS provides you with the skills you need to save their life.
Pediatric Advanced Life Support is a series of skills and techniques necessary for saving the lives of infants and children. If you are ever in a situation where a small child is choking or struggling to breathe or may be unconscious, PALS provides you with the skills you need to save their life.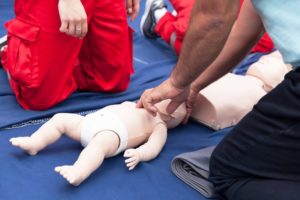 Next, let’s focus on a key area of PALS training and certification. This is the PALS algorithm, which looks similar to a tree diagram or chart.
Next, let’s focus on a key area of PALS training and certification. This is the PALS algorithm, which looks similar to a tree diagram or chart. First aid is the medical attention provided to a victim of an injury. This is a treatment that takes place where the injury happened, or on the scene. First aid is also administered as soon as possible. Therefore, first aid training gives you the skills needed to apply first aid applications.
First aid is the medical attention provided to a victim of an injury. This is a treatment that takes place where the injury happened, or on the scene. First aid is also administered as soon as possible. Therefore, first aid training gives you the skills needed to apply first aid applications.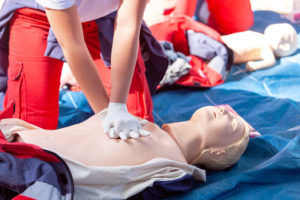 The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) is responsible for reducing personal injury in the workplace and for rules for the healthcare of workers.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) is responsible for reducing personal injury in the workplace and for rules for the healthcare of workers.  The role of an EMT involves taking care of patients in an emergency setting. In addition, there are different levels of emergency medical technicians. As you begin your career in this field of the healthcare industry, you will be an EMT-Basic. “An EMT, also known as an EMT-Basic, cares for patients at the scene of an incident and while taking patients by ambulance to a hospital. An EMT has the skills to assess a patient’s condition and to manage respiratory, cardiac, and trauma emergencies,” states the
The role of an EMT involves taking care of patients in an emergency setting. In addition, there are different levels of emergency medical technicians. As you begin your career in this field of the healthcare industry, you will be an EMT-Basic. “An EMT, also known as an EMT-Basic, cares for patients at the scene of an incident and while taking patients by ambulance to a hospital. An EMT has the skills to assess a patient’s condition and to manage respiratory, cardiac, and trauma emergencies,” states the  According to
According to  When someone has a heart rate that is too low, this is lower than 60 beats per minute. Keep in mind, that if you are dealing with an athlete, they may have a lower heart rate. However, the general rule is any time a heart rate is less than 60, the person is suffering from bradycardia. The person may be exhibiting signs of a low heart rate. These symptoms include fainting spells, shortness of breath, and feeling dizzy when standing.
When someone has a heart rate that is too low, this is lower than 60 beats per minute. Keep in mind, that if you are dealing with an athlete, they may have a lower heart rate. However, the general rule is any time a heart rate is less than 60, the person is suffering from bradycardia. The person may be exhibiting signs of a low heart rate. These symptoms include fainting spells, shortness of breath, and feeling dizzy when standing. The heart is the most important organ in a person’s body. Without a heart, a patient is unable to live due to a lack of blood and oxygen pumping and being circulated throughout the body. Brain-dead patients are living on life support, for example, and patients get by every day without an arm or leg.
The heart is the most important organ in a person’s body. Without a heart, a patient is unable to live due to a lack of blood and oxygen pumping and being circulated throughout the body. Brain-dead patients are living on life support, for example, and patients get by every day without an arm or leg.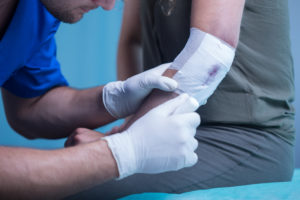 For those who are employed in occupations involving blood contact with the public, OSHA has set a
For those who are employed in occupations involving blood contact with the public, OSHA has set a  Whether you work as a pharmacy technician, patient care worker, or registered nurse, you will be able to use these credit hours toward renewing your state license. You can also apply these credits and this certificate to your application for a healthcare board exam. Continue to excel in learning about the latest in healthcare industry standards by earning your Bloodborne Pathogens Completion Certificate from AMC today.
Whether you work as a pharmacy technician, patient care worker, or registered nurse, you will be able to use these credit hours toward renewing your state license. You can also apply these credits and this certificate to your application for a healthcare board exam. Continue to excel in learning about the latest in healthcare industry standards by earning your Bloodborne Pathogens Completion Certificate from AMC today. To be a CMA in medical assisting, students must train to conduct a variety of hands-on skills that are involved with this occupation. Certified medical assistants work in the medical industry. Their skills are needed by upper-level medical professionals. The types of medical assisting skills that CMAs must utilize include:
To be a CMA in medical assisting, students must train to conduct a variety of hands-on skills that are involved with this occupation. Certified medical assistants work in the medical industry. Their skills are needed by upper-level medical professionals. The types of medical assisting skills that CMAs must utilize include: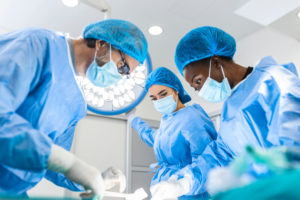 Individuals who are interested in administrative jobs at hospitals or working in healthcare facilities should consider a career as a medical assistant. This is a generalized work area that is lower down on the totem pole of medical professionals. You do not have to spend 10 or 15 years of training in medicine or $300,000 on tuition costs. Instead, getting certified as a medical assistant takes about one year. Timewise, the road to becoming a medical assistant is a lot shorter than that of a medical doctor.
Individuals who are interested in administrative jobs at hospitals or working in healthcare facilities should consider a career as a medical assistant. This is a generalized work area that is lower down on the totem pole of medical professionals. You do not have to spend 10 or 15 years of training in medicine or $300,000 on tuition costs. Instead, getting certified as a medical assistant takes about one year. Timewise, the road to becoming a medical assistant is a lot shorter than that of a medical doctor. PALS megacodes are training modules to help health care professionals practice before they put treatment modalities into action. As infants and children are less capable of saving themselves in a life-threatening situation, adult responders must be fully prepared to provide them with PALS and care.
PALS megacodes are training modules to help health care professionals practice before they put treatment modalities into action. As infants and children are less capable of saving themselves in a life-threatening situation, adult responders must be fully prepared to provide them with PALS and care. Now let’s take a close look at the most recent updates for the PALS megacodes. The International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (ILCOR) makes megacode updates every five years like clockwork. The most recent year for
Now let’s take a close look at the most recent updates for the PALS megacodes. The International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (ILCOR) makes megacode updates every five years like clockwork. The most recent year for