- Recognize Respiratory Distress or Failure
- Respond to Respiratory Distress/Failure
Recognize Respiratory Distress or Failure
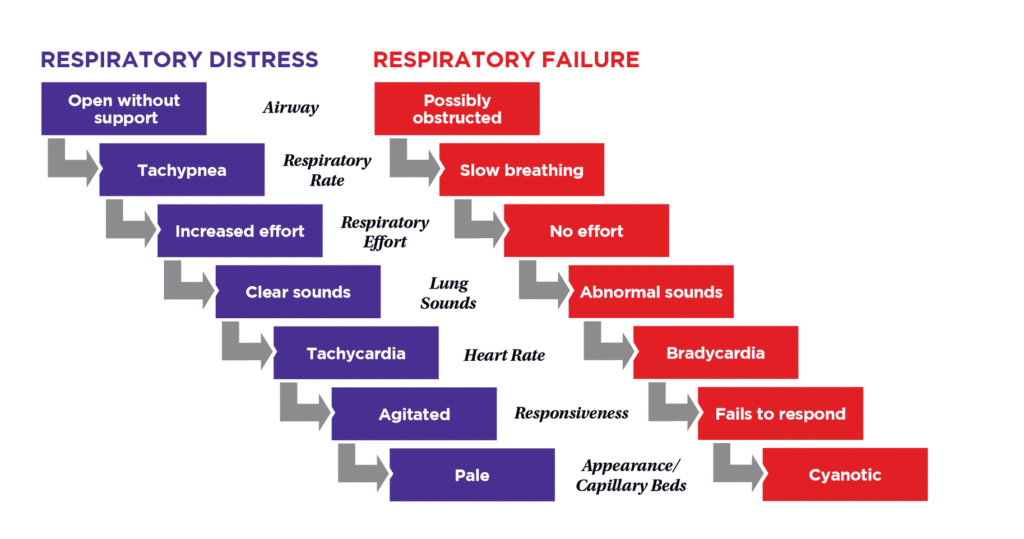
In its simplest form, respiratory distress is a condition in which pulmonary activity is insufficient to bring oxygen to and to remove carbon dioxide from the blood. Challenge arises with the recognition of respiratory distress when the person appears to be breathing but is not actually breathing effectively. Proper rate and depth of breathing is important to assess when evaluating whether the person is effectively breathing. The two main actions involved in breathing are ventilation and oxygenation. Consider the signs and symptoms presented below.
| VENTILATION | ||
|---|---|---|
| Is the airway clear? | Are the muscles of the chest functioning? | Is the rate of breathing sufficient? |
| Ex. An obstructed airway prevents gas flow | Ex. Chest muscle fatigue can occur | Ex. CNS depression can slow/stop breathing |
| OXYGENATION | ||
|---|---|---|
| Is oxygen available? | Is lung blood flow adequate? | Can gases cross the pulmonary vasculature? |
| Ex. High altitudes have low O2 | Ex. Vascular shunts may not send blood to lungs | Ex. Pulmonary edema or pneumonia |
Abnormal breath sounds
| STRIDOR | • Upper airway obstruction (foreign body) |
| GRUNTING | • Upper airway obstruction (Swollen airway) • Pneumonia (grunting to recruit alveoli) |
| WHEEZING | • Lower airway obstruction (Asthma) |
| CRACKLES | • Fluid in lungs (Wet), Atelectasis (Dry) |
| ABSENT/DECREASED BREATH SOUNDS | • Collapsed lung (air, blood) • Lung tissue disease (pneumonia) |
In some instances, breath sounds can provide information about the source of the breathing problem.
CAUSES OF RESPIRATORY DISTRESS/FAILURE
Respiratory distress or failure generally falls into one of four broad categories (Table 12): upper airway, lower airway, lung tissue disease, and central nervous system (CNS) issues. This list is not comprehensive, and specific conditions should be addressed with specific therapy; but these represent the most common causes of respiratory distress or failure in a pediatric population.
| UPPER AIRWAY | LOWER AIRWAY | LUNG TISSUE DISEASE | CNS ISSUES |
|---|---|---|---|
| Croup (swelling) | Bronchiolitis | Pneumonia | Overdose |
| Foreign body | Asthma | Pneumonitis | Head trauma |
| Retropharyngeal abscess | Pulmonary edema | ||
| Anaphylaxis |


