Management of Respiratory Distress and Respiratory Failure
| INITIAL MANAGEMENT OF RESPIRATORY DISTRESS/FAILURE | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Airway | Open and support the airway | Suction | Consider advanced airway |
| Breathing | Monitor O2 sats | Supplemental O2 | Nebulizers |
| Circulation | Monitor vitals | Establish vascular access | |
Table 13
Take Note
- Croup management is dependent on the degree of the disease.
- Dexamethasone, a type of corticosteroid, can cause hypertension and reduce activation of lymphocytes.
The degree of the condition controls the employment of PALS in cases of respiratory distress/failure. For example, bronchodilator inhalers are sufficient when treating mild asthma. However, ET intubation is required for treating severe asthma (status asthmaticus). The patient’s circumstances and situation must be taken into account for a more appropriate treatment.
Croup Management
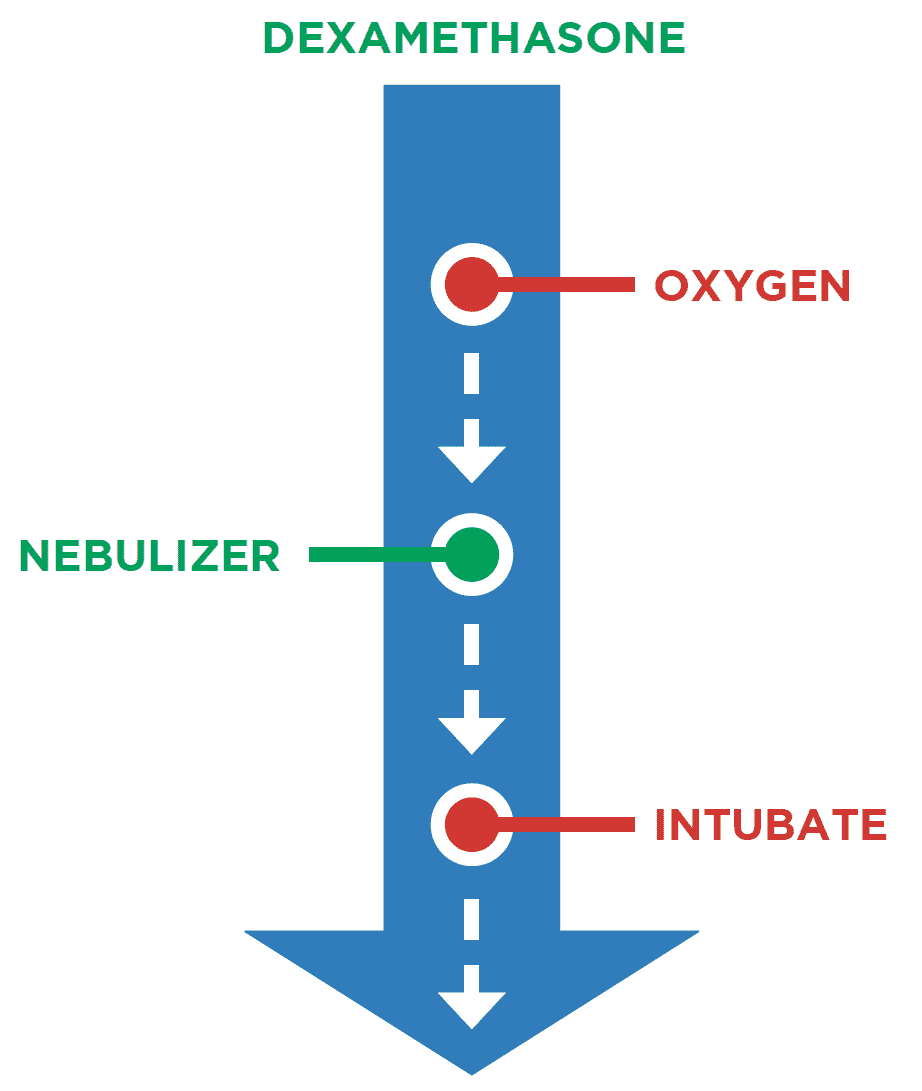
Figure 12
| Upper Airway | Lower Airway | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cause | Treatment | Cause | Treatment |
| CROUP |
|
BRONCHIOLITIS |
|
| FOREIGN BODY |
|
ASTHMA |
|
| ANAPHYLAXIS |
|
||
| Lung Tissue Disease | CNS Issues | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cause | Treatment | Cause | Treatment |
| PNEUMONIA |
|
OVERDOSE |
|
| PNEUMONITIS |
|
TRAUMA |
|
| PULMONARY EDEMA |
|
||
Table 14
Take Note
- Providers generally work their way up from the least invasive intervention to the most invasive one.
- For evidently more severe cases, it is recommended to perform more aggressive treatment methods
- To start bronchodilation, albuterol is commonly administered via nebulizer.
- Mycoplasma pneumonia, Haemophilus influenza, Chlamydia pneumonia, and Streptococcus pneumonia are among the agents of acute community-acquired pneumonia.
- Intense fever usually causes quiet tachypnea.
