ACLS Rhythms and Interpretation
STEP 1: RECAP THE PQRST PROPERTIES

Figure 8b
| PROTOTYPICAL ECG TRACING | |
| P-wave | Electrical activity is traveling through the atria. Synonymous with atrial depolarization. Reflects atrial contraction. |
| QRS Complex |
Electrical activity is traveling through the ventricles. Depolarization of the left and right ventricles. Reflects ventricular contraction. |
| T-wave | Synonymous with ventricular repolarization. Reflects the start of ventricular relaxation. |
| PR Interval | Onset of the P-wave to the start of the QRS complex. Reflects conduction through the atrioventricular (AV) node. |
| PR Segment | End of the P-wave to the start of the QRS complex. Reflects time delay between atrial and ventricular activation. |
| ST Interval | Onset of the S-wave to the start of the T-wave. Reflects initial, slow phase of ventricular repolarization. |
| ST Segment | End of the S-wave (J point) to the start of the T-wave. Reflects ventricular repolarization. |
| QT Interval | Onset of the QRS complex to the end of the T-wave. Reflects the period between ventricular depolarization and ventricular repolarization. |
| TP Interval | Onset of the T wave to the end of the P-wave. Reflects a period of electrical inactivity. |
| RR Interval | Reflects time elapsed between two successive R-waves of the QRS. |
STEP 2: IDENTIFY THE COMMON CATEGORIES OF ACLS RHYTHMS WITH A FEW EXAMPLES
Sinus Rhythms:
- Normal sinus rhythm (NSR)
- Sinus bradycardia
- Sinus tachycardia
Bradyarrhythmia and Conduction Blocks:
- 1st degree AV block
- 2nd degree AV block Type I (Mobitz Type I, Wenckebach’s)
- 2nd degree AV block Type II (Mobitz Type II)
- 3rd degree AV block (complete heart block, CHB)
Tachyarrhythmias:
- Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT)
- Wide-complex tachycardias
Pulseless Rhythms:
- Pulseless ventricular tachycardia (vTach)
- Ventricular fibrillation (vFib)
- Pulseless electrical activity (PEA)
- Asystole
Atrial Dysrhythmias:
- Atrial flutter
- Atrial fibrillation (aFib)
STEP 3: IDENTIFY THE MOST COMMON ACLS RHYTHMS
Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR)
- Normal P-wave
- Normal QRS Complex
- Normal T-wave
- HR: 60-100 BPM (at rest)
- Treatment: None
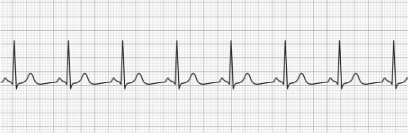
Sinus Bradycardia
- Normal P-wave
- Normal QRS Complex
- Normal T-wave
- HR: <60 BPM (at rest)
- Treatment (Symptomatic): Atropine, Dopamine (infusion), Epinephrine (infusion)
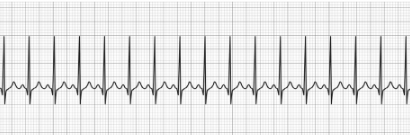
Sinus Tachycardia
- Normal P-wave
- Normal QRS Complex
- Normal T-wave
- HR: >100 BPM (at rest)
- Treatment: Reverse underlying condition (fever, anxiety, exercise), beta-blockers (metoprolol, sotalol)
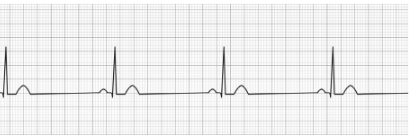
1st Degree Heart Block
- Prolonged PR interval due to delay in AV signal transmission
- P-wave may be buried in the preceding T-wave
- Treatment: Transcutaneous pacing (only indicated if prolongation of the PR interval is >400 ms)
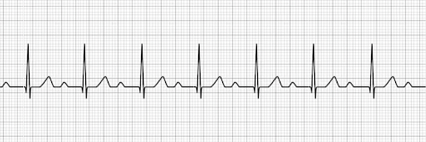
2nd Degree AV Block Type I (Mobitz Type I, Wenckebach’s)
- Progressive lengthening of the PR interval
- Progression occurs until the QRS complex is dropped
- Treatment: Atropine, Dopamine, Transcutaneous pacing
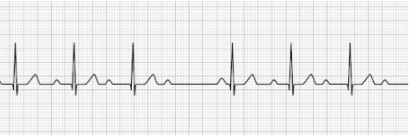
2nd Degree AV Block Type II (Mobitz Type II)
- PR interval is > 0.20 seconds and consistent (not gradually getting longer) but drops a beat, generally on a pattern of 3:1 or 4:1
- Treatment: Transcutaneous pacing
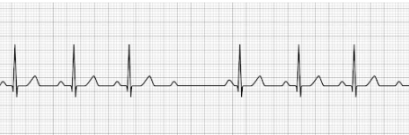
3rd Degree AV Block (complete heart block, CHB)
- No identifiable relationship between the P-wave and QRS waves
- P-P intervals are normal but do not relate to the QRS complex
- Treatment: Transcutaneous pacing
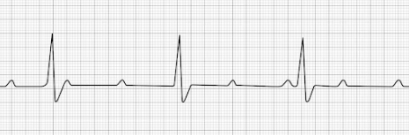
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)
- Profoundly rapid atrial rhythm with narrow QRS complexes
- Occurs when the signal impulse originates over the bundle branches
- HR: 150-250 BPM
- Treatment: Vagal maneuvers, Adenosine, synchronized cardioversion
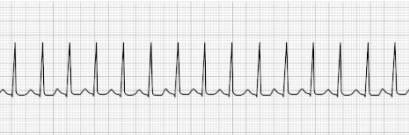
Atrial Fibrillation (aFib)
- Uniquely characterized by an absence of P-waves before the QRS complex
- HR: Highly irregular with significant fluctuation
- Treatment: beta-blockers (Metoprolol, Sotalol, etc.), Ca++ channel blockers
(Diltiazem, Verapamil, etc.), Digoxin, synchronized cardioversion.
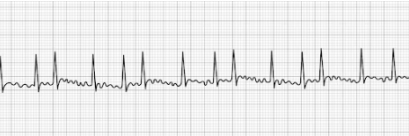
Atrial Flutter
- Uniquely characterized by a saw-toothed flutter appearance
- Toothed fluttering represents multiple P-waves for a single QRS complex
- Treatment: synchronized cardioversion, beta-blockers (Metoprolol, Sotalol, etc.),
Ca++ channel blockers (Diltiazem, Verapamil, etc), Digoxin.
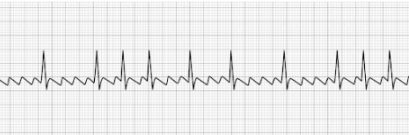
Ventricular Tachycardia (vTach)
- Abnormally-patterned wide QRS complex
- No P-waves
- High likelihood of rapid deterioration to a state of ventricular fibrillation
(vFib) - Often responsive to electrical defibrillation
- HR: >100 BPM
- Treatment: Defibrillation
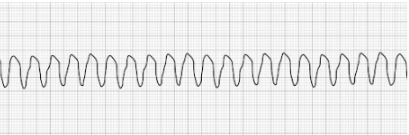
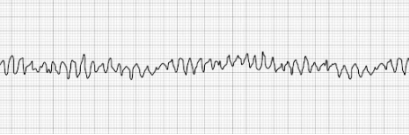
Pulseless Ventricular Fibrillation (vFib)
- Characterized by a chaotic wave pattern
- Patient has no palpable pulse
- Treatment: Defibrillation, epinephrine, amiodarone, lidocaine HCl